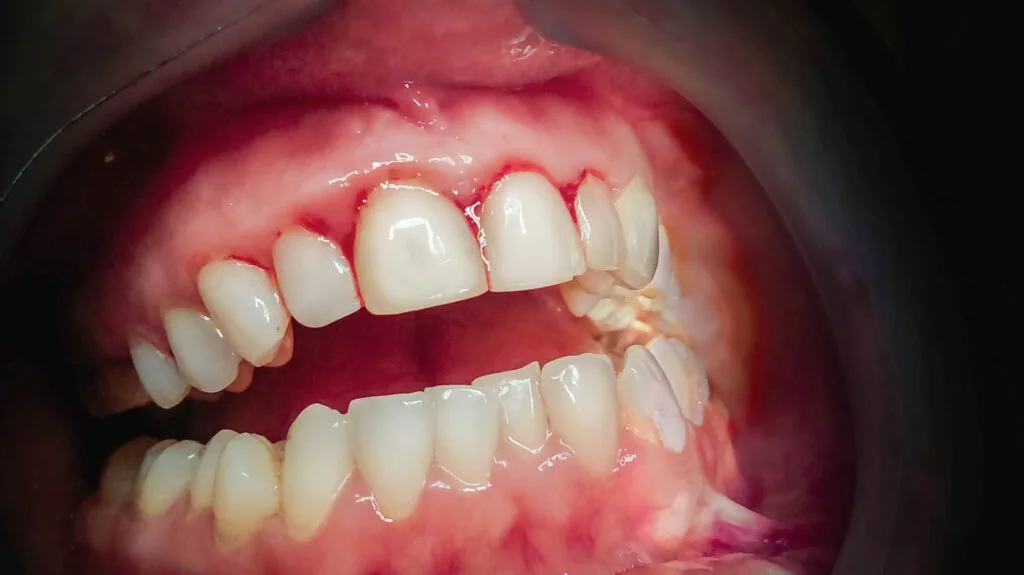
Gingivitis is the earliest stage of gum disease (periodontal disease). It involves inflammation of the gums caused by a buildup of plaque—a sticky film of bacteria that forms on your teeth and gums. Gingivitis is common but reversible with good oral hygiene.
Causes of Gingivitis
Gingivitis is primarily caused by the accumulation of plaque, but several factors can contribute:
- Poor oral hygiene (leading to plaque buildup)
- Smoking or chewing tobacco
- Poor nutrition, particularly lack of vitamin C
- Certain medications that cause dry mouth
- Medical conditions like diabetes, certain viral infections, or HIV/AIDS
- Family history of gum disease
- Stress and lack of sleep
- Age (more common in adults)
🦷 Signs and Symptoms
Early-stage gingivitis may not cause noticeable discomfort, but common signs include:
- Red, swollen, or puffy gums
- Bleeding gums, especially when brushing or flossing
- Bad breath (halitosis)
- Receding gums or tender gums
- Gums that are shiny or bleed easily
- Gum sensitivity
⚙️ Diagnosis
A dentist or hygienist will diagnose gingivitis by:
- Visual examination of the gums
- Measurement of gum pocket depths (the space between teeth and gums)
- Checking for bleeding while probing or brushing
🛠️ Treatment for Gingivitis
The good news is that gingivitis is reversible if caught early. Treatments include:
1. Professional Cleaning
- Scaling and root planing: Removes plaque and tartar from above and below the gumline.
- Cleaning may be needed more frequently if gingivitis is more advanced.
2. Improved Oral Hygiene
- Brushing twice a day with fluoride toothpaste
- Flossing daily to remove plaque from between teeth
- Antibacterial mouthwash (to kill bacteria and reduce plaque)
3. Lifestyle Changes
- Quit smoking (smoking is a major risk factor)
- Eat a balanced diet, including foods rich in vitamin C
4. Regular Dental Check-ups
- Professional cleanings every 6 months, or more often if advised by your dentist
🏥 Preventing Gingivitis
To avoid gingivitis and more severe gum disease, follow these tips:
- Brush with a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste
- Floss daily to clean areas brushing misses
- Rinse with mouthwash regularly, especially if you have dry mouth
- Regular dental visits (every 6 months or as recommended)
⚠️ Consequences of Untreated Gingivitis
If gingivitis is not treated, it can progress into periodontitis, a more serious form of gum disease that can lead to:
- Tooth loss
- Infection of the gums and bone
- Receding gums
- Abscesses
✅ Prognosis
- Gingivitis is completely reversible with proper treatment
- Regular maintenance and healthy habits help prevent recurrence

