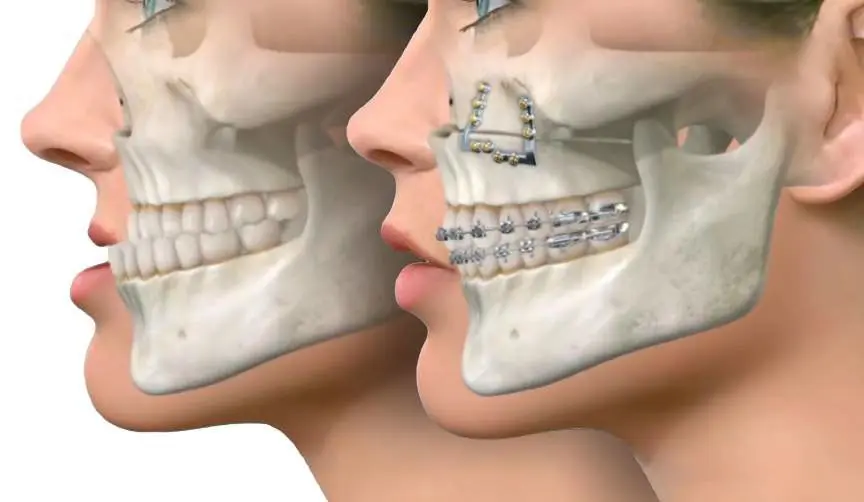
Orthognathic surgery is a type of corrective jaw surgery performed to address skeletal and dental irregularities that cannot be resolved with orthodontics alone. It involves repositioning the upper jaw (maxilla), lower jaw (mandible), or both to improve function, appearance, and overall facial harmony.
When Is Orthognathic Surgery Needed?
Orthognathic surgery may be recommended for:
- Severe overbite, underbite, or open bite
- Facial asymmetry or imbalance
- Sleep apnea caused by jaw structure
- Chronic jaw pain or temporomandibular joint (TMJ) issues
- Difficulty chewing, speaking, or swallowing
- Congenital jaw abnormalities
- Injury-related jaw misalignment
🛠️ Types of Orthognathic Surgery
1. Maxillary Osteotomy
- Repositions the upper jaw
- Used for open bite, crossbite, or protruding/receded upper jaw
2. Mandibular Osteotomy
- Repositions the lower jaw
- Corrects underbite or receded lower jaw
3. Bimaxillary Osteotomy
- Involves both upper and lower jaws
- Used for complex bite or alignment issues
4. Genioplasty
- Repositions or reshapes the chin
- Often combined with other jaw procedures
📋 Procedure Overview
- Orthodontic Preparation (Pre-Surgery Braces)
- Lasts 12–18 months to align teeth for the new jaw position
- Surgery
- Performed under general anesthesia in a hospital
- Usually takes 2–4 hours depending on the complexity
- Hospital Stay
- 1–3 days post-surgery
- Recovery
- Initial recovery: 2–4 weeks
- Full healing: up to 12 months
- Post-op orthodontics to fine-tune bite
✅ Benefits of Orthognathic Surgery
- Balanced facial appearance
- Improved bite and chewing
- Better speech and breathing
- Long-term jaw joint health
- Boost in confidence and comfort

