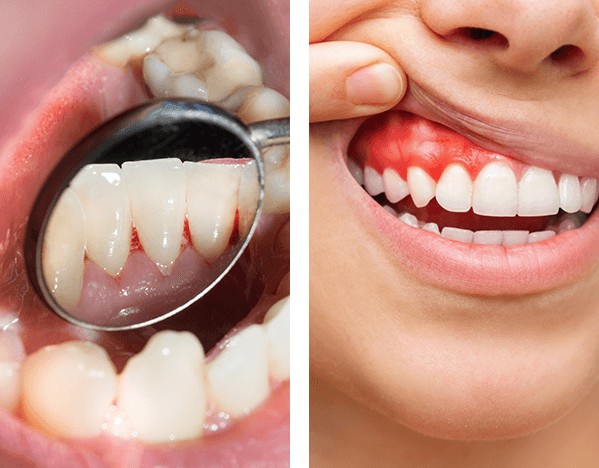
Gum treatment is a dental procedure or series of procedures used to treat gum disease (gingivitis or periodontitis) and restore gum health. It aims to remove infection-causing bacteria, reduce inflammation, and prevent tooth loss.
Types of Gum Disease
- Gingivitis: The earliest stage of gum disease, characterized by inflammation, redness, and bleeding of the gums. It is usually reversible with proper oral hygiene and professional treatment.
- Periodontitis: A more severe form of gum disease that occurs when gingivitis is left untreated. It involves the destruction of the supporting structures of the teeth, including the bone, and can lead to tooth loss.
Signs and Symptoms of Gum Disease
- Red, swollen, or tender gums
- Bleeding while brushing or flossing
- Receding gums
- Persistent bad breath
- Loose or shifting teeth
- Painful chewing
Treatment Options
- Non-Surgical Treatments
- Professional Cleaning: Regular dental cleanings are essential for preventing and treating gingivitis. During a cleaning, the dentist or hygienist removes plaque and tartar from the teeth and gum line.
- Scaling and Root Planing: A deep cleaning procedure performed under local anesthesia. Scaling removes plaque and tartar from above and below the gum line, while root planing smooths the tooth roots to help the gums reattach to the teeth.
- Antibiotics: Topical or oral antibiotics can be used to control bacterial infection. These may be applied directly to the gums or taken as a pill or capsule.
- Surgical Treatments
- Flap Surgery (Pocket Reduction Surgery): Involves lifting back the gums to remove tartar deposits in deep pockets and then suturing the gums back into place. This reduces pocket depth and makes it easier to keep the area clean.
- Bone Grafts: Used to replace bone destroyed by periodontitis. The grafts may be made from the patient’s own bone, donated bone, or synthetic materials. This procedure helps promote the regrowth of natural bone.
- Soft Tissue Grafts: Used to cover exposed roots or augment thin gums. Tissue is usually taken from the roof of the mouth and stitched to the affected gum area.
- Guided Tissue Regeneration: A technique that involves placing a special fabric between the bone and gum tissue to encourage bone and connective tissue regrowth.
- Laser Therapy: Lasers can be used to remove diseased tissue and bacteria, reduce pocket size, and encourage the reattachment of gums to teeth.
Preventive Measures
- Good Oral Hygiene: Brushing twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and flossing daily to remove plaque between teeth and under the gum line.
- Regular Dental Visits: Professional cleanings and check-ups at least twice a year to detect and treat early signs of gum disease.
- Healthy Diet: Eating a balanced diet low in sugar and high in nutrients that promote gum health, such as vitamin C and calcium.
- Avoiding Tobacco: Smoking and using tobacco products increase the risk of gum disease and can hinder treatment.
Importance of Treating Gum Disease
Treating gum disease is crucial not only for oral health but also for overall health. Untreated gum disease has been linked to various systemic conditions, including:
- Heart disease
- Stroke
- Diabetes
- Respiratory disease
- Complications during pregnancy

